Bootstrap Modal Popup
Intro
From time to time we absolutely need to make the focus on a individual info remaining everything others lowered behind making certain we've obtained the website visitor's mind or perhaps have plenties of info needed to be easily accessible from the webpage still, so vast it undoubtedly will bore and push back the ones checking over the webpage.
For these sorts of occurrences the modal component is basically valuable. What it engages in is featuring a dialog box using a large area of the screen diming out whatever other things.
The Bootstrap 4 framework has all the things needed for generating this type of element by having minimal efforts and a helpful direct development.
Bootstrap Modal is streamlined, though variable dialog prompts powered via JavaScript. They assist a variety of use cases beginning at user alert to fully custom-made web content and come with a number of helpful subcomponents, sizes, and more.
Information on how Bootstrap Modal Position behaves
Before starting by using Bootstrap's modal component, be sure to review the following for the reason that Bootstrap menu decisions have already replaced.
- Modals are developed with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They are actually placed above anything else located in the document and remove scroll from the
<body>- Selecting the modal "backdrop" will automatically close the modal.
- Bootstrap just supports just one modal window at a time. Embedded modals usually are not maintained given that we believe them to be bad user experiences.
- Modals use
position:fixeda.modal- One once more , because of
position: fixed- In conclusion, the
autofocusContinue reviewing for demos and usage suggestions.
- Because of how HTML5 specifies its own semantics, the autofocus HTML attribute comes with no result in Bootstrap modals. To obtain the equal effect, put into action some custom-made JavaScript:
$('#myModal').on('shown.bs.modal', function ()
$('#myInput').focus()
)To start we need to get a switch on-- an anchor or button to be clicked so the modal to become shown. To execute in this way simply specify
data-toggle=" modal"data-target="#myModal-ID"Instruction
Now let us develop the Bootstrap Modal in itself-- first we require a wrapper component providing the whole thing-- specify it
.modalA good idea would most likely be at the same time bring in the
.fadeYou would most likely additionally want to include the similar ID which you have already determined in the modal trigger due to the fact that usually if those two do not match the trigger won't really shoot the modal up.
Additionally you might actually wish to include a close switch within the header assigning it the class
.closedata-dismiss="modal"Essentially this id the design the modal components have inside the Bootstrap framework and it pretty much has remained the very same in both Bootstrap version 3 and 4. The new version comes with a lot of new ways though it seems that the developers team thought the modals function all right the way they are in this way they made their attention out of them so far.
Now, lets have a look at the different sorts of modals and their code.
Modal elements
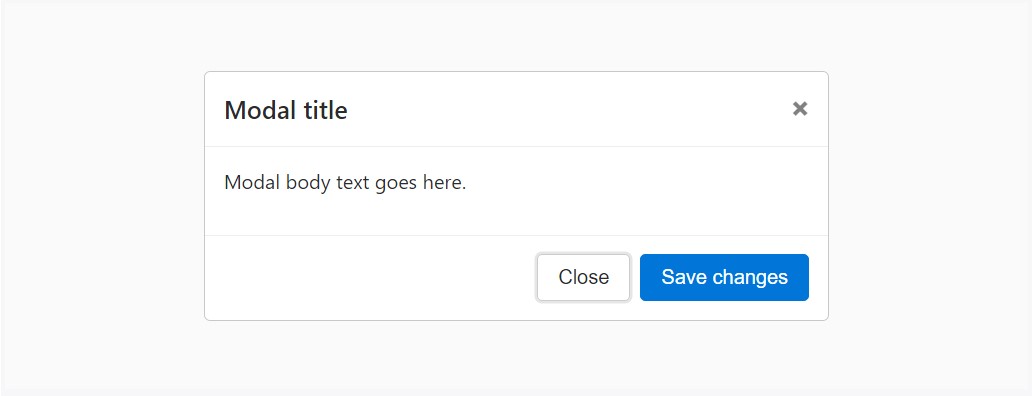
Here is a static modal sample ( representing its
positiondisplay<div class="modal fade">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<p>Modal body text goes here.</p>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Live test
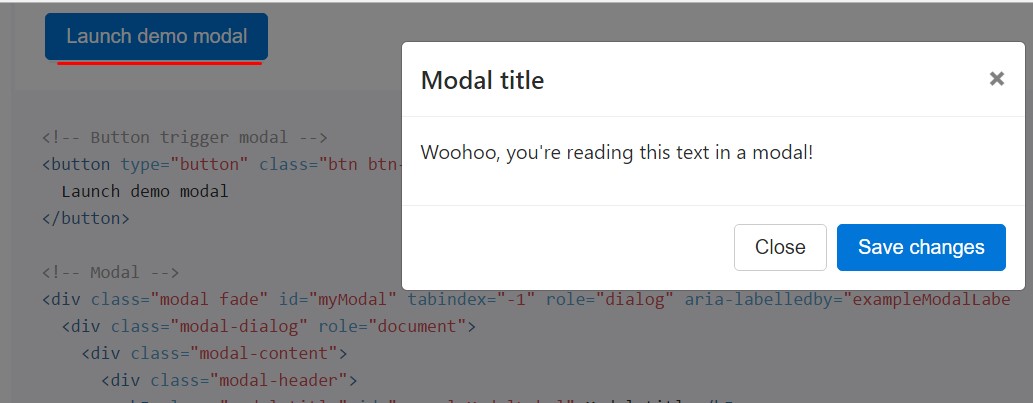
In case that you will use a code listed below - a functioning modal demo is going to be generated as showned on the pic. It will definitely slide down and fade in from the very top of the webpage.
<!-- Button trigger modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal">
Launch demo modal
</button>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="myModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Scrolling expanded content
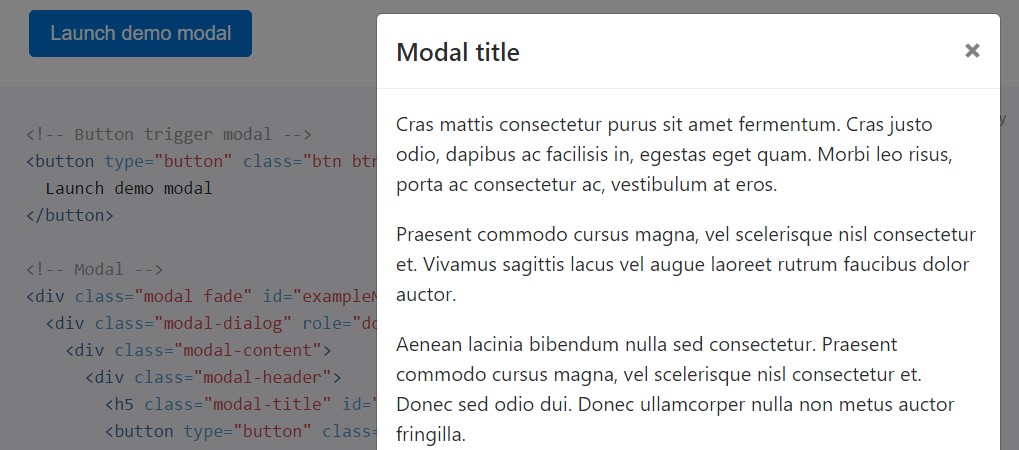
As modals end up being way too long toward the user's viewport or tool, they scroll independent of the page itself. Work the test below to notice things that we point to ( additional reading).
<!-- Button trigger modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModalLong">
Launch demo modal
</button>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="exampleModalLong" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLongTitle" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLongTitle">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Tooltips and also popovers
Tooltips and popovers can absolutely be localised inside of modals just as needed. Once modals are closed, any tooltips and popovers inside are as well immediately rejected.
<div class="modal-body">
<h5>Popover in a modal</h5>
<p>This <a href="#" role="button" class="btn btn-secondary popover-test" title="Popover title" data-content="Popover body content is set in this attribute.">button</a> triggers a popover on click.</p>
<hr>
<h5>Tooltips in a modal</h5>
<p><a href="#" class="tooltip-test" title="Tooltip">This link</a> and <a href="#" class="tooltip-test" title="Tooltip">that link</a> have tooltips on hover.</p>
</div>Applying the grid
Implement the Bootstrap grid system in a modal by nesting
.container-fluid.modal-body
<div class="modal-body">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4 col-md-offset-4">.col-md-4 .col-md-offset-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3 col-md-offset-3">.col-md-3 .col-md-offset-3</div>
<div class="col-md-2 col-md-offset-4">.col-md-2 .col-md-offset-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3">.col-md-6 .col-md-offset-3</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-9">
Level 1: .col-sm-9
<div class="row">
<div class="col-8 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-8 .col-sm-6
</div>
<div class="col-4 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-4 .col-sm-6
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>A variety of modal material
Contain a bunch of buttons that generate the very same modal using a little bit separate contents? Apply
event.relatedTargetdata-*Listed here is a live demo followed by example HTML and JavaScript. For additional information, read through the modal events docs with regard to specifics on
relatedTarget
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@mdo">Open modal for @mdo</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@fat">Open modal for @fat</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@getbootstrap">Open modal for @getbootstrap</button>
<div class="modal fade" id="exampleModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">New message</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="recipient-name" class="form-control-label">Recipient:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="recipient-name">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="message-text" class="form-control-label">Message:</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="message-text"></textarea>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Send message</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>$('#exampleModal').on('show.bs.modal', function (event)
var button = $(event.relatedTarget) // Button that triggered the modal
var recipient = button.data('whatever') // Extract info from data-* attributes
// If necessary, you could initiate an AJAX request here (and then do the updating in a callback).
// Update the modal's content. We'll use jQuery here, but you could use a data binding library or other methods instead.
var modal = $(this)
modal.find('.modal-title').text('New message to ' + recipient)
modal.find('.modal-body input').val(recipient)
)Pull out animation
For modals that simply show up instead fade into view, take off the
.fade<div class="modal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="..." aria-hidden="true">
...
</div>Dynamic heights
In the event that the height of a modal changes while it is open, you need to command
$(' #myModal'). data(' bs.modal'). handleUpdate()Availableness
Setting YouTube web videos
Inserting YouTube video recordings in modals needs additional JavaScript not within Bootstrap to immediately stop playback and even more.
Extra sizes
Modals feature two optional sizes, provided by using modifier classes to get placed on a
.modal-dialog
<!-- Large modal -->
<button class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target=".bd-example-modal-lg">Large modal</button>
<div class="modal fade bd-example-modal-lg" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="myLargeModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-lg">
<div class="modal-content">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Small modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target=".bd-example-modal-sm">Small modal</button>
<div class="modal fade bd-example-modal-sm" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="mySmallModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-sm">
<div class="modal-content">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>Handling
The modal plugin toggles your unseen web content as needed, by using data attributes or JavaScript. It also adds in
.modal-open<body>.modal-backdropUsing files attributes
Turn on a modal without crafting JavaScript. Set up
data-toggle="modal"data-target="#foo"href="#foo"<button type="button" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#myModal">Launch modal</button>Via JavaScript
Call a modal with id
myModal$('#myModal'). modal( options).Possibilities
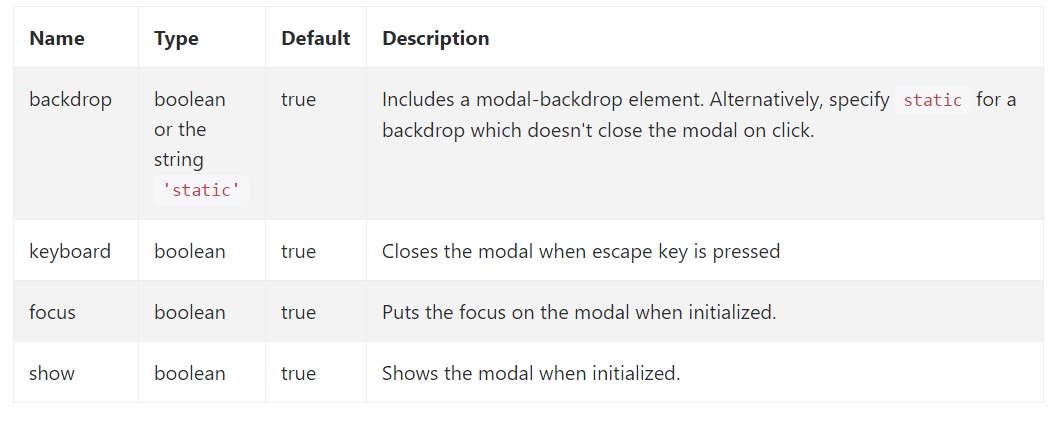
Opportunities may possibly be passed through details attributes or JavaScript. For information attributes, append the option name to
data-data-backdrop=""Examine also the image below:
Approaches
.modal(options)
.modal(options)Triggers your web content as a modal. Accepts an extra options
object$('#myModal').modal(
keyboard: false
).modal('toggle')
.modal('toggle')Manually toggles a modal.
$('#myModal').modal('toggle').modal('show')
.modal('show')Manually launches a modal. Returns to the caller just before the modal has really been demonstrated (i.e. before the
shown.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('show').modal('hide')
.modal('hide')Manually covers up a modal. Come back to the caller right before the modal has actually been covered (i.e. just before the
hidden.bs.modal$('#myModal').modal('hide')Bootstrap modals events
Bootstrap's modal class exposes a number of events for netting in to modal performance. All modal events are fired at the modal itself (i.e. at the
<div class="modal">
$('#myModal').on('hidden.bs.modal', function (e)
// do something...
)Final thoughts
We found out ways in which the modal is made but what could possibly be within it?
The answer is-- basically everything-- coming from a long words and aspects plain paragraph with a few headings to the very complicated system which with the adaptive design approaches of the Bootstrap framework might literally be a web page inside the web page-- it is technically attainable and the option of implementing it falls to you.
Do have in your mind though if at a certain point the material as being poured into the modal gets far excessive it's possible the better strategy would be putting the whole element inside a separate webpage for you to receive more or less greater appearance along with application of the entire display screen size available-- modals a pointed to for smaller sized blocks of web content urging for the viewer's interest .
Review a few on-line video guide regarding Bootstrap modals:
Linked topics:
Bootstrap modals: official documents

W3schools:Bootstrap modal short training
Bootstrap 4 with remote modal